数据集与样本难度度量
本文分享关于数据集与样本难度度量的论文,具体为:
- A Theory of Usable Information Under Computational Constraints
- Understanding Dataset Difficulty with \(\mathcal{V}\)-Usable Information
主要内容来自于组会分享,slides 可点此查看。
1. 香农互信息
在概率论和信息论中,两个随机变量的互信息(Mutual Information,MI)度量了两个变量之间相互依赖的程度。具体来说,对于两个随机变量,MI是一个随机变量由于已知另一个随机变量而减少的“信息量”(单位通常为比特)。
离散随机变量 X 和 Y 的互信息可以计算为:
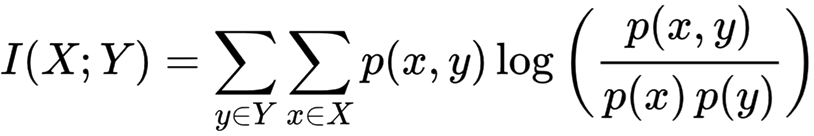
其中 p(x, y) 是 X 和 Y 的联合概率质量函数,而 p(x) 和 p(y) 分别是 X 和 Y 的边缘概率质量函数。
互信息又可以等价地表示成:
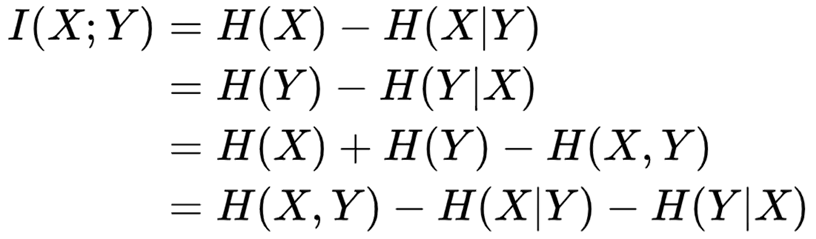
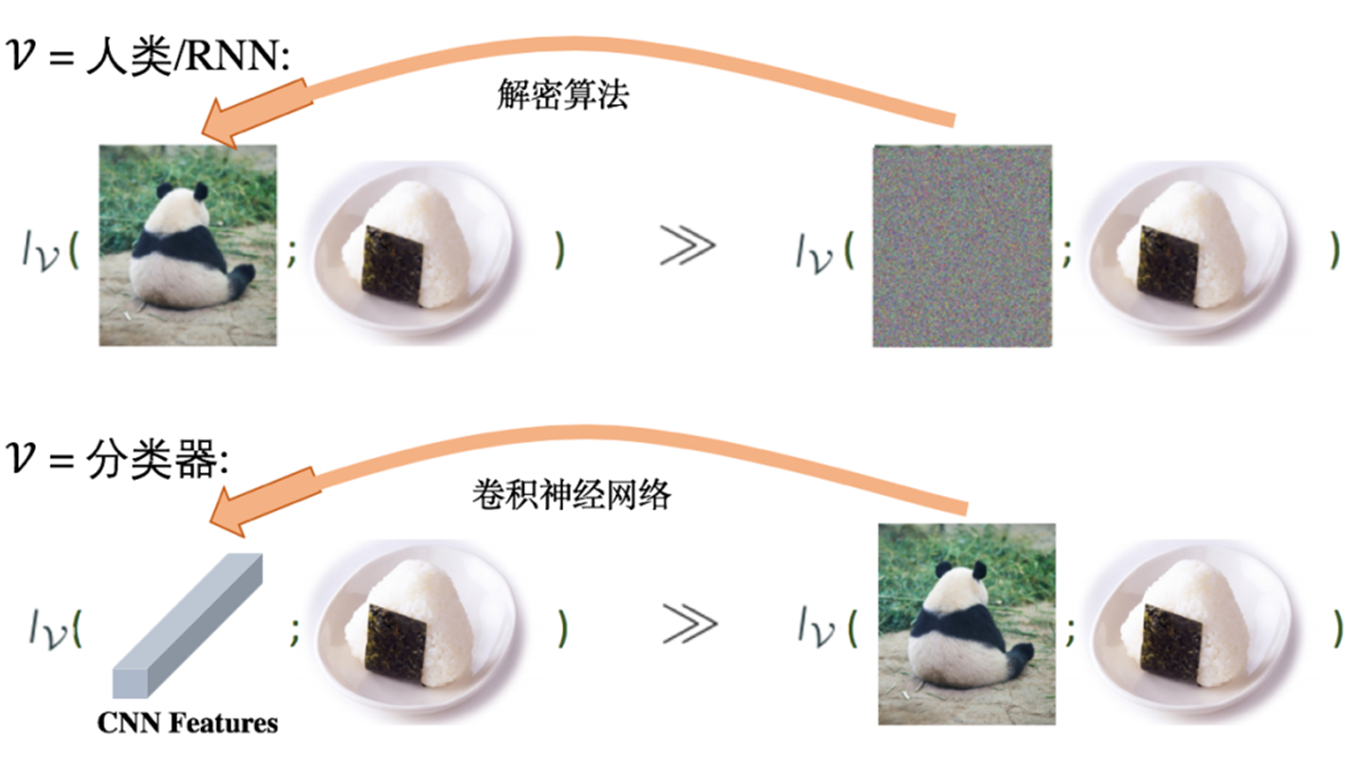
但是,在机器学习场景下,香农互信息与我们目前的一些经验性认识存在冲突,比如下面图片展示的例子:

在香农互信息理论下,明文与标注的互信息 和 密文与标注的互信息 相等。但是,对于我们人类而言,从明文能够轻易识别出标注;而不能够根据密文判断标注。即如下图所示:

为了解决这一冲突,作者提出了新的概念:考虑计算约束下的互信息。
2. 对香农互信息的扩展定义——\(\mathcal{V}\)-Information
首先,作者引入三个概念:
predictive family
Let \(\Omega=\{f: \mathcal{X} \cup\{\varnothing\} \rightarrow \mathcal{P}(\mathcal{Y})\}\). We say that \(\mathcal{V} \subseteq \Omega\) is a predictive family if it satisfies \[ \forall f \in \mathcal{V}, \forall P \in \operatorname{range}(f), \quad \exists f^{\prime} \in \mathcal{V}, \quad \text { s.t. } \quad \forall x \in \mathcal{X}, f^{\prime}[x]=P, f^{\prime}[\varnothing]=P \]
predictive conditional \(\mathcal{V}\)-entropy
Let \(X, Y\) be two random variables taking values in \(\mathcal{X} \times \mathcal{Y}\), and \(\mathcal{V}\) be a predictive family. Then the predictive conditional \(\mathcal{V}\)-entropy is defined as \[ \begin{aligned} H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid X) & =\inf _{f \in \mathcal{V}} \mathbb{E}_{x, y \sim X, Y}[-\log f[x](y)] \\ H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid \varnothing) & =\inf _{f \in \mathcal{V}} \mathbb{E}_{y \sim Y}[-\log f[\varnothing](y)] \end{aligned} \] We additionally call \(H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid \varnothing)\) the \(\mathcal{V}\)-entropy, and also denote it as \(H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y)\) .
predictive conditional \(\mathcal{V}\)-information
Let \(X, Y\) be two random variables taking values in \(\mathcal{X} \times \mathcal{Y}\), and \(\mathcal{V}\) be a predictive family. The predictive \(\mathcal{V}\)-information from \(X\) to \(Y\) is defined as \[ I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y)=H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid \varnothing)-H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid X) \]
\(\mathcal{V}\)-information 有以下一些性质:
基本性质
Let \(Y\) and \(X\) be any random variables on \(\mathcal{Y}\) and \(\mathcal{X}\), and \(\mathcal{V}\) and \(\mathcal{U}\) be any predictive families, then we have
- Monotonicity: If \(\mathcal{V} \subseteq \mathcal{U}\), then \(H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y) \geq H_{\mathcal{U}}(Y), H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid X) \geq H_{\mathcal{U}}(Y \mid X)\).
- Non-Negativity: \(I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y) \geq 0\).
- Independence: If \(X\) is independent of \(Y, I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y)=I_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \rightarrow X)=0\).
数据处理不等式(与香农互信息不同)
- Shannon Mutual Information: Letting \(t: \mathcal{X} \rightarrow \mathcal{X}\) be any function, \(t(X)\) cannot have higher mutual information with \(Y\) than \(X: I(t(X) ; Y) \leq I(X ; Y)\).
- \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information: Denoting \(t\) as the decryption algorithm and \(\mathcal{V}\) as a class of natural language processing functions, we have that: \(I_{\mathcal{V}}(t(X) \rightarrow Y)>I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y) \approx 0\).
不对称性(与香农互信息不同)
If \(\mathcal{V}\) contains all polynomial-time computable functions, then \(I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow h(X)) \gg I_{\mathcal{V}}(h(X) \rightarrow X)\) , where \(h: \mathcal{X} \rightarrow \mathcal{Y}\).
根据 \(\mathcal{V}\)-information 的性质,我们就能够合理解释上面例子展示的问题,从而有:
上面介绍的是 \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information 的严格定义,但是在机器学习中,我们不存在真实的分布,而是仅有从分布上采样的有限大小的数据集。下面,作者要解决如何在有限大小的数据集上估计 \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information:
Let \(X, Y\) be two random variables taking values in \(\mathcal{X}, \mathcal{Y}\) and \(\mathcal{D}=\left\{\left(x_i, y_i\right)\right\}_{i=1}^N \sim X, Y\) denotes the set of samples drawn from the joint distribution over \(\mathcal{X}\) and \(\mathcal{Y} . \mathcal{V}\) is a predictive family. The empirical \(\mathcal{V}\)-information (under \(\mathcal{D}\) ) is the following \(\mathcal{V}\)-information under the empirical distribution defined via \(\mathcal{D}\) : \[ \hat{I}_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y ; \mathcal{D})=\inf _{f \in \mathcal{V}} \frac{1}{|\mathcal{D}|} \sum_{y_i \in \mathcal{D}} \log \frac{1}{f[\varnothing]\left(y_i\right)}-\inf _{f \in \mathcal{V}} \frac{1}{|\mathcal{D}|} \sum_{x_i, y_i \in \mathcal{D}} \log \frac{1}{f\left[x_i\right]\left(y_i\right)} \] Then we have the following PAC bound over the empirical \(\mathcal{V}\)-information:
Assume \(\forall f \in \mathcal{V}, x \in \mathcal{X}, y \in \mathcal{Y}, \log f[x](y) \in[-B, B]\). Then for any \(\delta \in(0,0.5)\), with probability at least \(1-2 \delta\), we have: \[ \left|I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y)-\hat{I}_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y ; \mathcal{D})\right| \leq 4 \mathfrak{R}_{|\mathcal{D}|}\left(\mathcal{G}_{\mathcal{V}}\right)+2 B \sqrt{\frac{2 \log \frac{1}{\delta}}{|\mathcal{D}|}} \] where we define the function family \(\mathcal{G}_{\mathcal{V}}=\{g \mid g(x, y)=\log f[x](y), f \in \mathcal{V}\}\), and \(\mathfrak{R}_N(\mathcal{G})\) denotes the Rademacher complexity of \(\mathcal{G}\) with sample number \(N\).
3. 使用 \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information 评估数据集和样本难度
利用上面介绍的 \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information 工具并进行实验,能够发现一些有趣的现象。
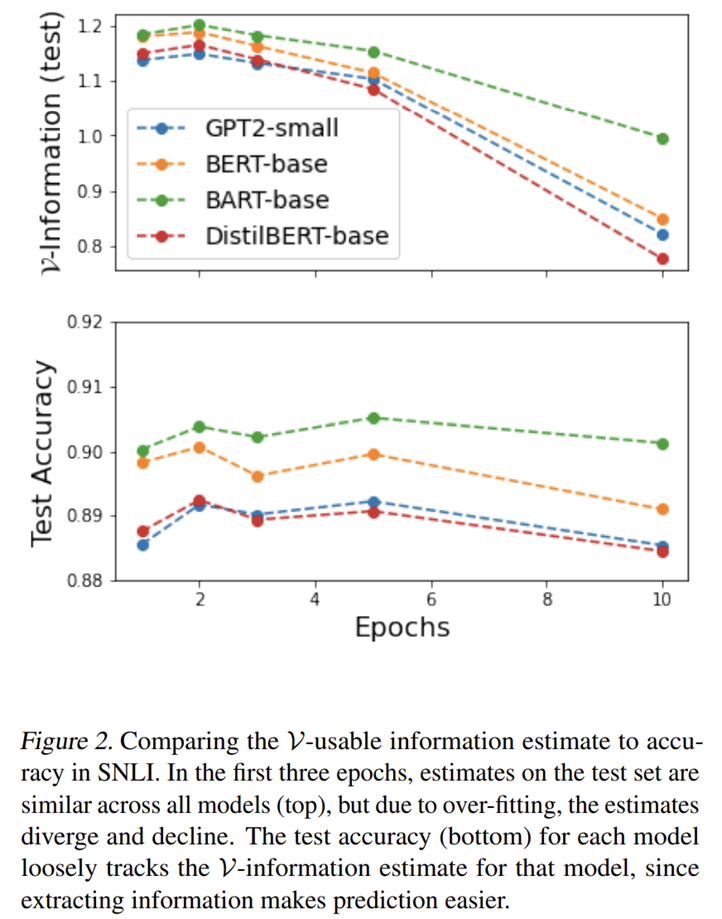
- 大模型 accuracy 与\(\mathcal{V}\)-Usable Information 都更高,因为提取更多的信息让识别更容易
- \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information 相比 accuracy 对过拟合更加敏感
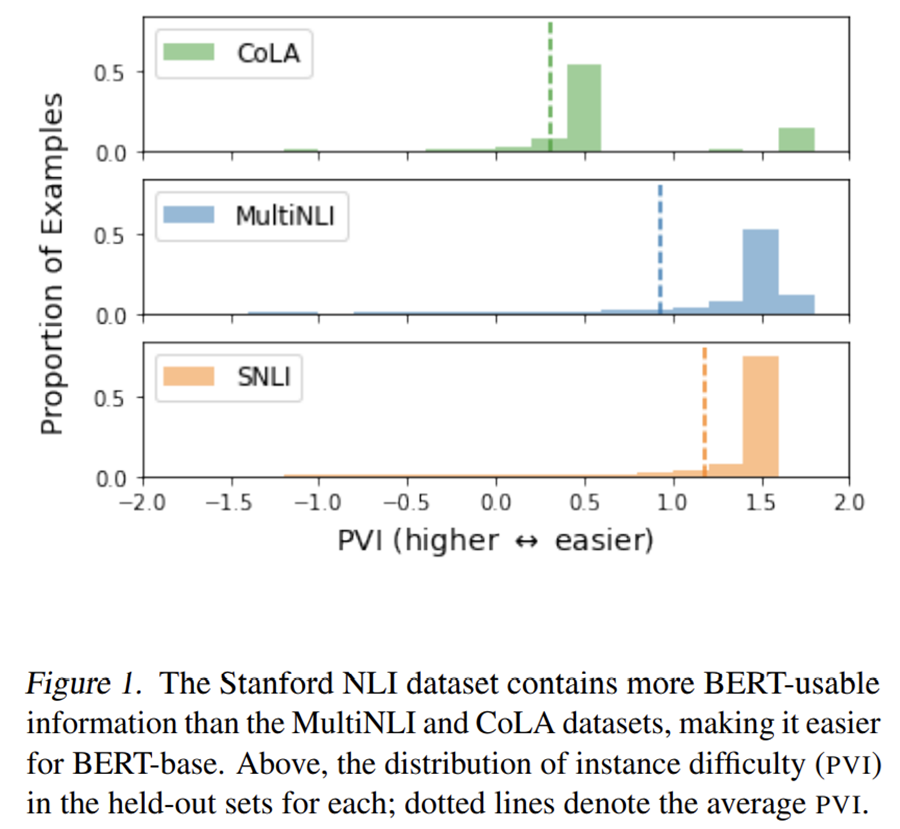
- 提供了衡量不同数据集难度的方法
然后,引入评估样本点 \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information (Pointwise \(\mathcal{V}\)-Information,PVI)的方法:
Given random variables \(X, Y\) and a predictive family \(\mathcal{V}\), the pointwise \(\mathcal{V}\)-information (PVI) of an instance \((x, y)\) is \[ \operatorname{PVI}(x \rightarrow y)=-\log _2 g[\varnothing](y)+\log _2 g^{\prime}[x](y) \] where \(g \in \mathcal{V}\) s.t. \(\mathbb{E}[-\log g[\varnothing](Y)]=H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y)\) and \(g^{\prime} \in \mathcal{V}\) s.t. \(\mathbb{E}\left[-\log g^{\prime}[X](Y)\right]=H_{\mathcal{V}}(Y \mid X)\).
PVI is to \(\mathcal{V}\)-information what PMI is to Shannon information: \[ \begin{aligned} I(X ; Y) & =\mathbb{E}_{x, y \sim P(X, Y)}[\operatorname{PMI}(x, y)] \\ I_{\mathcal{V}}(X \rightarrow Y) & =\mathbb{E}_{x, y \sim P(X, Y)}[\operatorname{PVI}(x \rightarrow y)] \end{aligned} \]
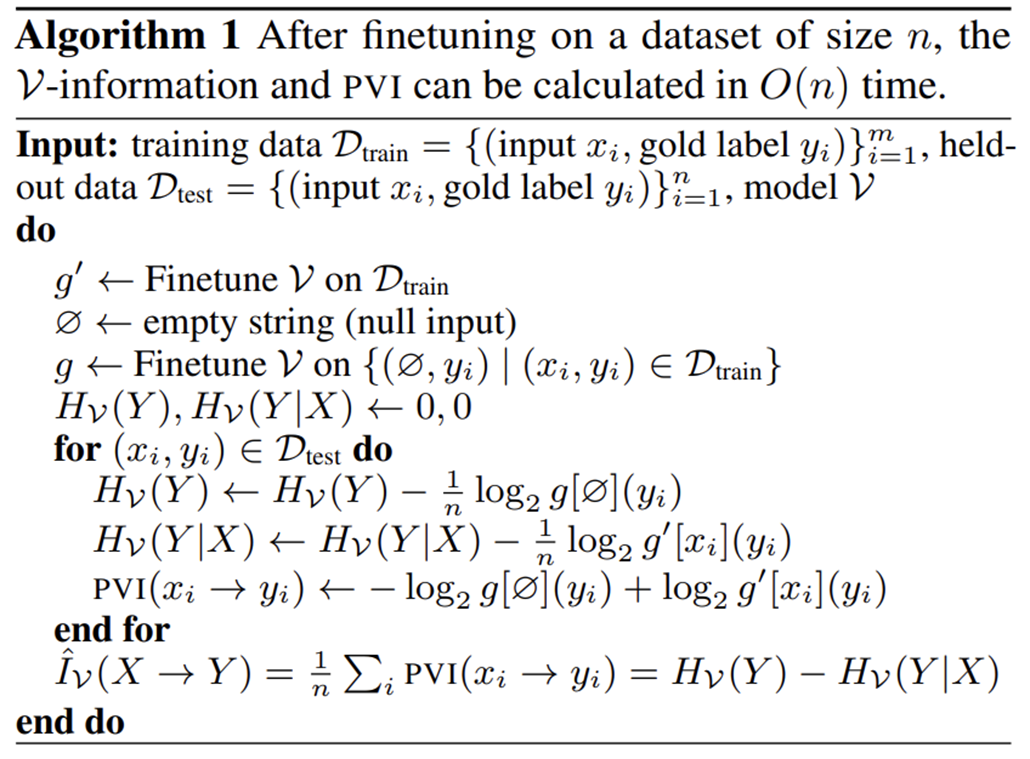
完整算法流程如下:
然后,利用 PVI 进行实验,同样可以观察到一些有趣的现象:
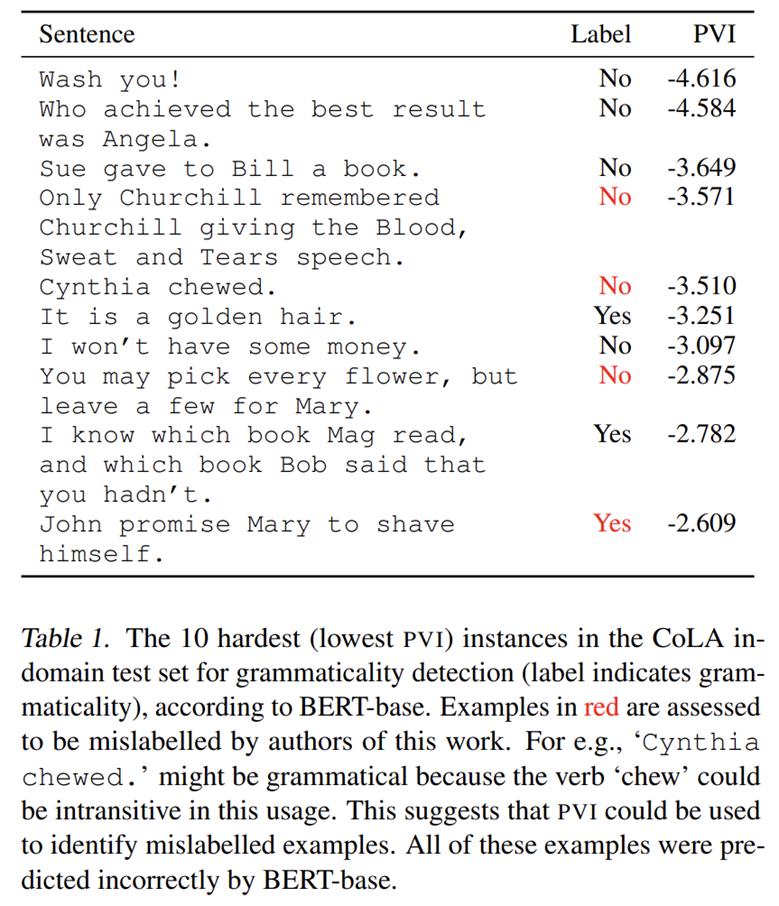
- PVI 最低的样本中存在不少标注错误
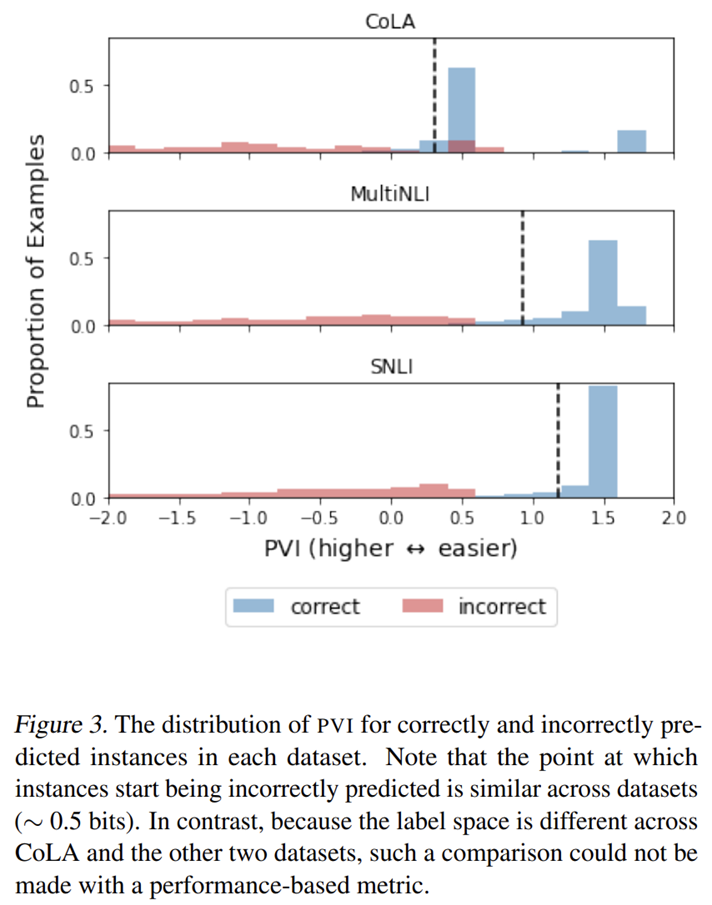
- 模型能够正确分类样本的 PVI 阈值在 0.5 左右
此外,原论文中还展示了一些有趣的实验现象,这里不再赘述,具体请参阅原论文。